
DNA can control the protein synthesis which changes characteristics so it indirectly affects many thing.Ī gene is defined as a sequence of bases on a DNA molecule coding for a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.#ĭNA is transcribed into RNA which is then translated into a protein. The base pairs can appear in any order along the DNA molecule so their sequence can encode information. A gene is simply a section of DNA around 1000-2000 base pairs long. The bases are protected on the inside and there are billions of hydrogen bonds making it a stable moleculeĭNA contains genes and genes control characteristics.
SUGAR PHOSPHATE BACKBONE IN DNA FREE
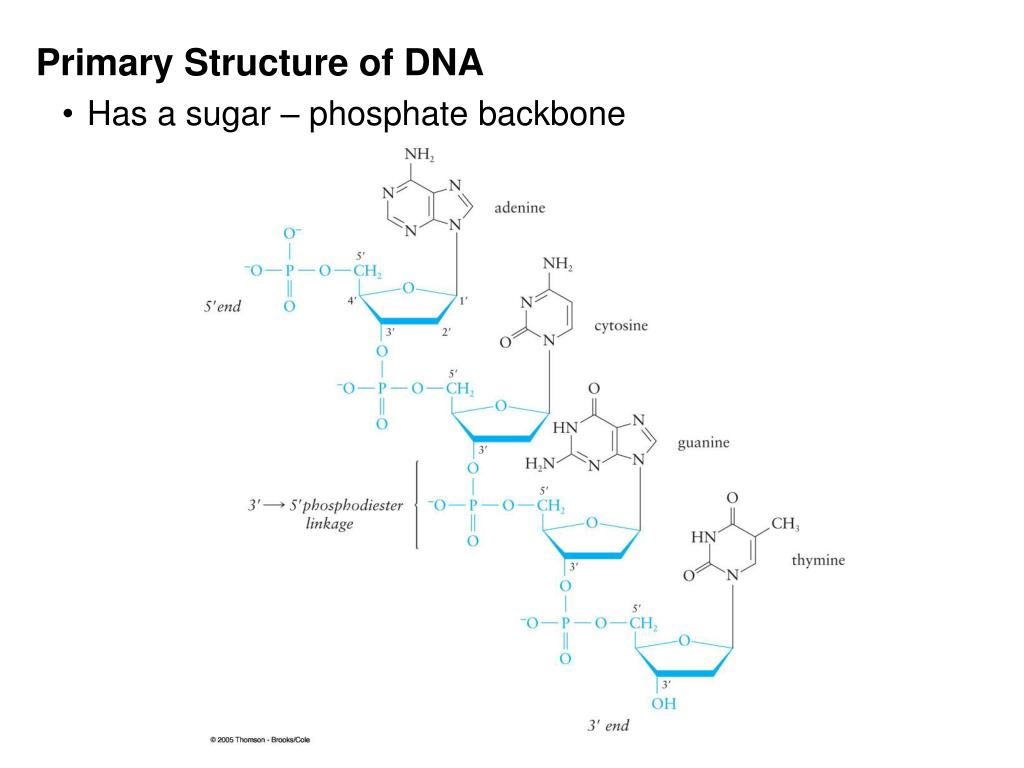
A polynucleotide has a free phosphate group at one end, called the 5 end as it is attached to the carbon 5 of the sugar and a free OH group on the other side coming out of the carbon 3 of the sugar Polymerisation ensures the sugar-phosphate backbone continues the structure. This is a condensation reaction (water is produced). Nucleotides polymerise by forming a phosphodiester bond between carbon 3 of the sugar and an oxygen atom of the phosphate. ATP is used as the energy transfer molecule while AMP is used as a messenger chemical These are very important and play more of a role then just DNA. So for instance you can have adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Nucleotides can have one, two or three phosphate groups. Pyrimidines are a sub-group of nitrogenous bases, these are one ringed which also have nitrogen within them.Purines are a sub-group of nitrogenous bases, these are two rings which have nitrogen within them.There are four different bases in DNA nucleotides called Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. These are small organic basic groups that contain the elements C,H,O,N.

Carbon 2 has a hydrogen atom – then the sugar is deoxyribose, found in DNA.Carbon 2 has a hydroxyl group – the sugar is ribose, found in RNA.Is a negatively charged ion and gives nucleic acids their acidic properties.
They are polymers composed of monomers called nucleotides. Understand the effect of point mutations on amino acid sequences, as illustrated by sickle cell anaemia in humansĭNA & RNA are nucleic acids (weak acids) and are found in the nuclei of cells.Understand the term gene mutation as illustrated by base deletions,insertions and substitutions.Understand the nature of the genetic code, including triples coding for amino acids,start and stop codons, degenerate and non overlapping nature and that not all the genome codes for proteins.Understand the processes oif transcription in the nucleus and translation at the ribosome, includiong the role of sense and anti-sense DNA, mRNA, tRNA and the ribosomes.Know the structure of tRNA, including nucleotides, the role of hydrogen bonds and the anticodon.Know the structure of mRNA including nucleotides, the sugar phosphate backbone and the role of the hydrogen bonds.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
